In a May 2024 communique, the student movement in Gaza issued a salute as well as a challenge to the global student movement. Published through the Palestinian Prisoner Solidarity Network, the statement acknowledged student organisations across the globe as ‘a revolutionary fighting vanguard, and a natural and integral part of our Palestinian Liberation movement’. Commending the student mobilisations which culminated in a wave of university encampments across Northern America in April, the Secretariat of Palestinian Student Frameworks in Gaza at the same time called for a ‘revolutionary escalation of the global student intifada for Palestine’.
Amidst the broadest and most sustained campaigns of international solidarity with Palestine witnessed in recent years, what grants students pride of place in the salutations, as well as exhortations, issued by the besieged in Gaza?
A ‘revolutionary vanguard’?
Next to the regional armed movements which provide the bulk of military and logistical support to the Palestinian struggle for national liberation, the Western student body is surely a marginal figure, at best playing an auxiliary role. Yet the encampments have highlighted the centrality of university campuses as key battlegrounds for Palestine solidarity in the global North, and perhaps even the potential of students to accede to the exacting title of a ‘revolutionary fighting vanguard’. To produce such a force though, the Western student movement must reckon with the conditions of its possibility as well as the contradictions of the present moment.
On the whole, it’s possible to characterise the current movement as an organic recomposition of at least three social forces or political valences present in the imperial core, each bearing a distinct historical stamp. First, it is a natural outgrowth of an anti-racism revitalised and radicalised in recent years by the George Floyd uprisings and the Black Lives Matter movements, as well as the protest camps of NODAPL Standing Rock. Second, it inherits decades of strident campaigning by the Palestinian diaspora and Boycott, Divestment, and Sanctions organising. Third, it has revived the legacy of student opposition to imperialist wars and Apartheid, most notably in Vietnam and South Africa. As Aziz Rana recently put it, this movement can be seen as marking an indisputable return of the ‘language of empire’ to public consciousness.
While the language of anti-imperialism and internationalism has no doubt returned, however, the material demands of these ideologies pose a real and formidable challenge to student movements in the North. In this regard, the Research and Destroy collective is correct in its assessment that the student intifada has to contend not only with state violence and secondary antagonists, but also with ‘the difficulty in the alignment of form and content, of tactics and goals, given its position as a solidarity movement distant from its primary antagonists and its primary purpose, the liberation of Palestine’. What the movement inherits and combines by way of anti-racist, BDS, and anti-war campaigning is by no means a guarantee of strategic efficacy.
From ‘anti-war’ to the people’s war
Despite the strong affinities built over the years between black, Indigenous, and Palestinian activists, this affinity has yet to translate into tangible and sustainable forms of internationalism. And while BDS has provided an effective strategy on several fronts, its impact is and continues to be blunted on others, not least that of the university-finance-military nexus. Thanks to the rise of asset management as a mode of enclosure and capital accumulation in recent decades, universities have been lavishly equipped with the means to out-manoeuvre student organisations and their already limited capacity to enforce and realise demands for divestment. Indeed, and as noted elsewhere, the challenge of divestment today often involves not so much specific investments in single companies as it does market performance in entire sectors, meaning that students are really faced with the entire architecture and ‘overarching system of finance capital guiding the ways their universities now accrue value.’
Moreover, while the language and clarion calls of the student movements of the 60’s and 70’s may still resonate with considerable force today, this resonance belies a telling ideological shortcoming. While struggles in Vietnam and Algeria inspired movements for peace in the West, they were received as a call for war in the Third World – namely a people’s war. The difference is striking, and it remains palpable today in the widely divergent aims and respective strategies employed to achieve them, including in the largely pacifist orientation of much Palestine solidarity organising in the West.
Finally, there is the reality of Israel today, which is neither Apartheid South Africa, or French Algeria, or even the US in Vietnam. It is rather the purest expression of militarised settler colonialism acting as a lynchpin of Western imperialism and fossil capitalism as a whole, and its fate has implications of world-systemic and world historical proportions. More than a geostrategic bulwark and forward base for the US empire, the Zionist state is a key and integral component of the cycle of capital accumulation in the region, described by Ali Kadri as ‘accumulation through waste’. Centred on the production and circulation of oil and weapons, this system ensures the recursive de-development and degradation of state capacities in the region, undercutting social reproduction on a societal scale. Far from being epiphenomenal, systemic destruction through instability and war is an elementary feature of this logic and, therefore, of the totality of capital. Israel plays several of key roles in securing the continuation of this cycle, including that of arms producer, geopolitical irritant, as well as a catalyst of region-wide militarisation.
These realities, and the challenges they pose, have not gone unnoticed by the wider student body. Calls for a ceasefire are only the most audible and visible demands of the movement, and underwriting them is an ideological shift which is likely to push the movement beyond the simple opposition to a genocidal war. As the encampments’ organising cadres have been at pains to highlight, Israel’s onslaught has been but a catalyst for a process that was already underway in the politicisation and conscientisation of a broad swathe of the student body in the US. A consequence of this has been the critical grasp on a fundamental quality of the world system which Israel embodies outright, and which makes opposition to it a material necessity and not just a moral imperative. This is the basic fact that core and periphery are interlocked through value flows which determine political, economic, and social life at the most intimate level.
The student’s movement beyond itself
Formalised into concrete and lasting strategy, this basic fact stands to make the student intifada a potent force indeed. To that effect, the groundwork has already been laid by the mobilisations across campuses worldwide. What distinguishes today’s student movement from those of yesteryear is that it has finally stood the critique of ‘financialisation’ the right way up. Since at least the turn of the century, financial capital has been identified by the Western left as its principal adversary, and successive waves of revolt have rallied under the banner of anti-austerity.
Within this vision, ‘neoliberalism’ has been, at best, understood as a capitalist broadside against labour, with finance acting as an instrument of plunder, despoliation, and new waves of enclosure. Vast, almost incalculable, transfers of wealth is both the goal and consequence, and where the periphery is taken into account, it does not complicate the picture so much as simply add a bottom layer to this upward transfer. For perhaps the first time in these two decades, a movement has now emerged in the North which is incorporating into practice an urgent corrective to this overall vision.
Unlike their predecessors, the current revolts on campus are not staged in protest to job cuts or student debt, but to the leveraging of universities as a link in the value chain between core and periphery. While it remains to be seen whether their momentum will be regained in the autumn term, the initial thrust of the encampments struck in the right direction, This struggle realises on the level of practice what has so often been posited only in theory. That is, that finance and the financialisation of higher education does not simply represent an attack on the ‘commons’ or a public good, but rather the acquisition and burning of social surpluses in the core to fuel the wasting and immolation of human lives in the periphery.
This process can doubtless be said to hold for any number of sectors and institutions commandeered by finance and ‘rentier capitalism’ in the North, but the extent to which its contradictions have been heightened and politicised on campuses seems unparalleled. Of course, this has much to do with the student’s contradictory position itself, which is somewhat ‘liberated’ from the fetters of the wage through the peonage of debt.
The political consequences for campuses are significant, with state repression dismantling one of the few traditional bastions for political organising left intact, if teetering, by neoliberalism. Whatever its outcome for universities, this unravelling crystallises a fundamental observation by organisers themselves, which is that the student activist is but a ‘transitional figure that ideally helps to broaden the movement for Palestinian liberation beyond itself from the campus as battlefield, generalising it into a struggle that engages with the material contradictions and antagonisms of society at large.’
Whither Palestine solidarity?
In this transitional process, it is not just the figure of the student whose destiny becomes manifest in its own dissolution. The question of Palestine ‘solidarity’ itself now meets a belated reckoning, its erstwhile self-evidence cracking under the historical force of Al-Aqsa’s Flood, and its faultlines revealing new depths and divergences. This is precisely as it should be: the Palestinian resistance has sought nothing less than to ‘crack history open’ and divulge the latent possibilities seemingly foreclosed by the hegemony of empire.
In the region itself, ‘normalisation’ named the total victory of fossil capitalism and systemic destruction. October 7th derailed this consensus and charted a different course, one which has recentered Palestine as the fulcrum of class struggle and which moreover insists on its final determinacy through what can only be described as a people’s war. The importance of the latter as a political project and strategic horizon cannot be over-stated, and its meaning has yet to become clear for Western solidarity movements. While it is unlikely that the resistance leadership fully anticipated the abyssal depths to which Israel would sink in exacting bloody retribution, the destructive and vindictive nature of the response was well within its expectations.
The Flood was nevertheless unleashed as an opening salvo of a war, the outcomes, stakes, and risks of which would implicate the masses of Palestine and the Arab world as a whole. The objectively incalculable cost incurred as a result is not the price of a negotiated ceasefire or a phased return to normalisation, but that of a concrete and calculated set of objectives which would give the resistance an advance position and a firmer footing in its anticipated popular war. These include but are not limited to: the liberation of a maximal number of Palestinian captives, the delegitimisation of the Vichy government of the Palestinian Authority, the undermining and demoralisation of Israel’s military and security apparatuses, and the deepening of its internal political crisis. These are the intended advances in a war of manoeuvre for which the resistance had been painstakingly preparing and capacity-building for years.
Across the West Bank and the wider region, the Flood continues to rally the masses and popular armed movements, crystallising political alignments and opening up new fronts of resistance. Beyond the region, however, such lines have yet to be drawn, and Palestine solidarity remains imprisoned in the form it acquired through its interminable war of position. If it is to have any meaningful role in the political terrain opened by the Flood, the solidarity movement must re-examine both its form and content in line with the people’s war, including its current objectives as well as its long-term ambitions.
In concrete terms, this will of course depend on a practical evaluation of the movement’s situation and conditions in any one locale. All the same, the task likely entails a reappraisal of some broad and characteristic features, which should provide the movement with a departure point rather than a terminus. Key among these is its spontaneity, which may have been a necessary condition for its emergence, but which is wholly insufficient for and antithetical to its continuation, let alone its escalation. Without a concerted political program giving it strategic and ideological clarity, the movement is unlikely to acquire a form adequate to the task at hand.
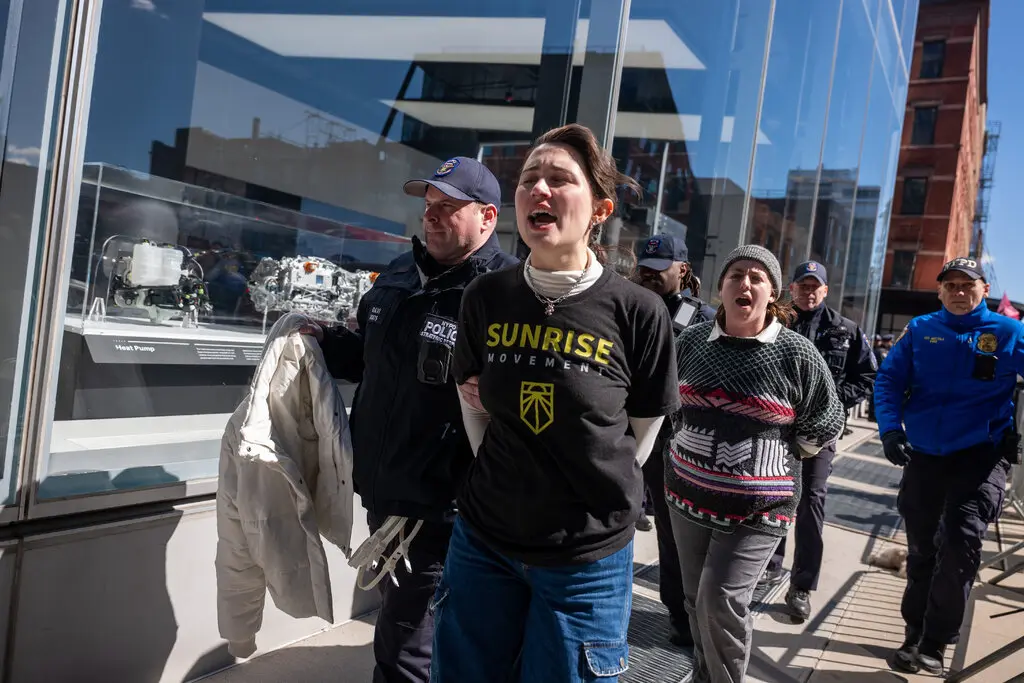
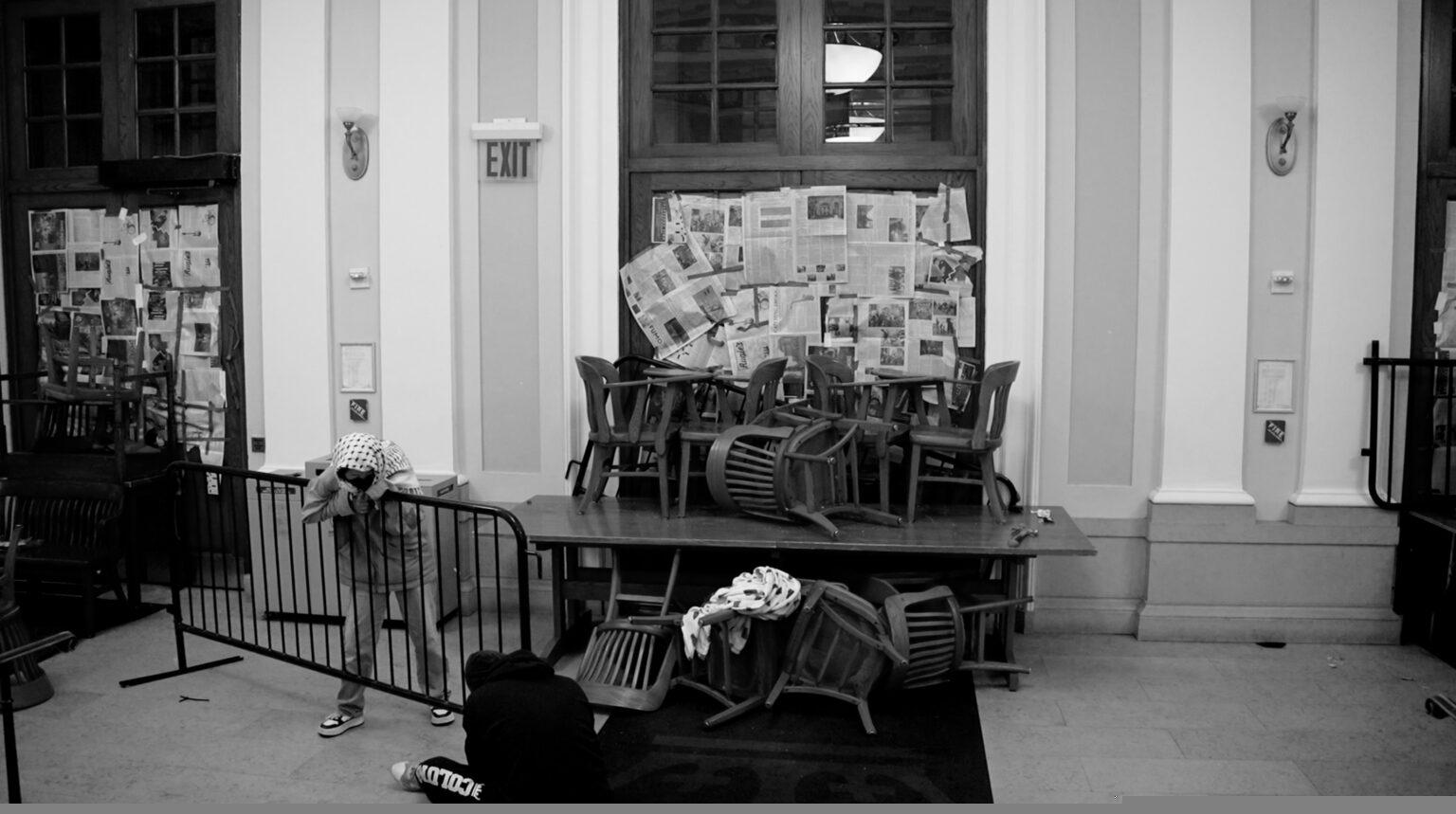
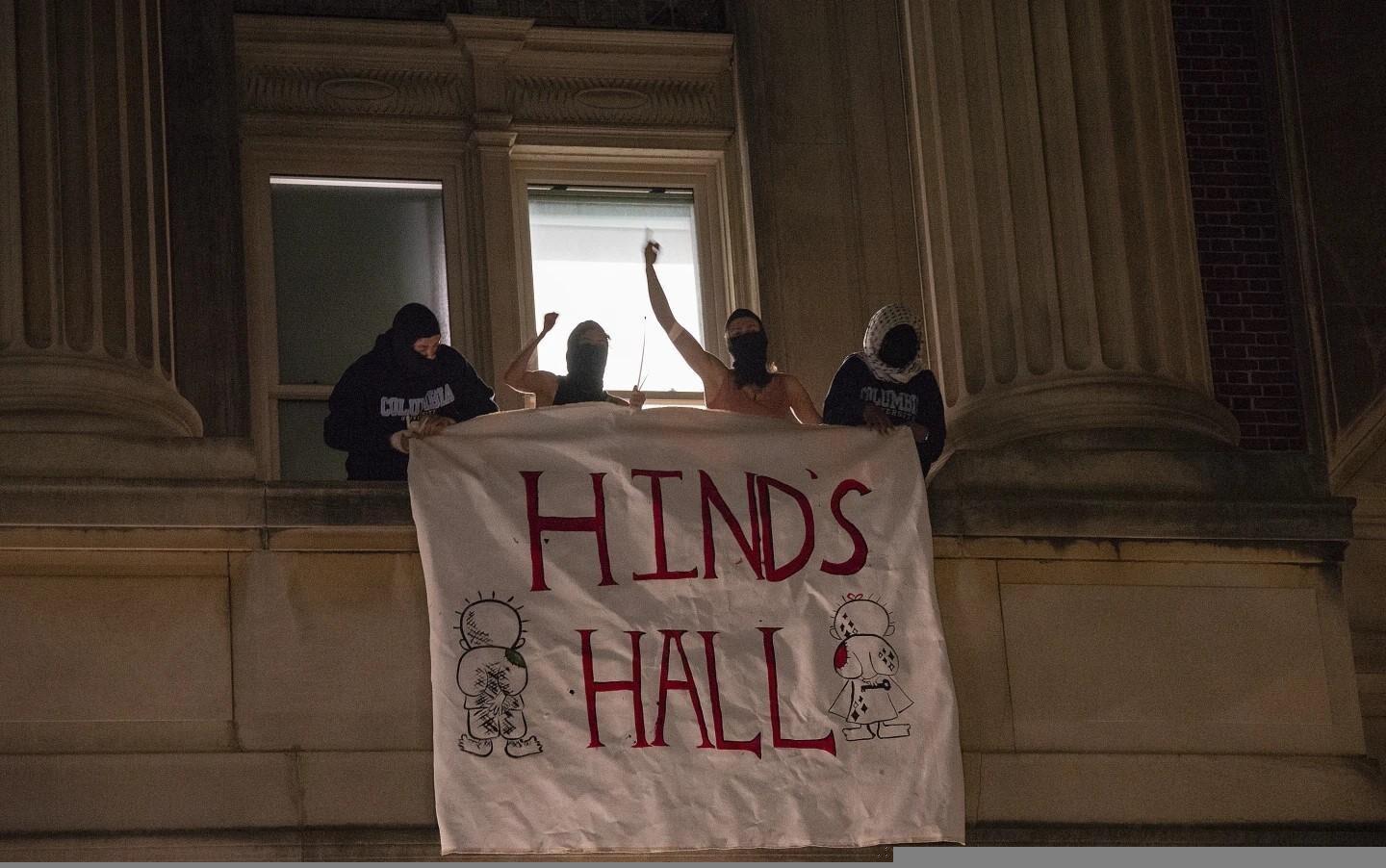
The university encampments, for instance, are paradigmatic in this regard. As a tactic which is naturally and necessarily contained, in terms of both space and time, the barricaded camp is potentially far-reaching if harnessed to a wider strategy within which disclosure and divestment campaigns are situated as initial or transitory phases. The camps could serve as both muster and training ground, bolstering the movement logistically and numerically, arming it politically and ideologically, and furnishing it with the organisational means to deploy beyond the camp itself. To date, however, this potential does not seem to have borne fruit. Whether through repression or concession or a combination, universities effectively dismantled the encampments within weeks of their emergence. But the end of the encampments need not have spelled a setback for the movement, which seems to be the case currently. It could have instead meant its expansion and re-deployment beyond campuses given a longer-term strategy with sufficient collective buy-in, successive phases for escalation, and/or multiple alternatives for redirection. In lieu of this, however, and once the disclosure and divestment campaigns reached a (rather predictable) impasse, the movement failed to initiate any manoeuvres to that effect.
At present, therefore, it appears that while the ‘student intifada’ has invigorated the Western solidarity movement and perhaps the left in general, it remains ill-equipped to rise to the challenge of escalation issued by Palestinian comrades. The failure to develop a political program can reasonably be attributed to a number of causes, all of them instructive. Of course, they include material challenges of forming broad and sustained coalitions in the context of a neoliberal, repressive, and Zionist university apparatus, but they also concern the class composition of the student body and the ideological consequences thereof. Both these dimensions and others deserve attention elsewhere, but it is worth noting in conclusion at least one precondition for escalated action.
Whether or not student organisations are really, truly answerable to their Palestinian comrades will likely depend on whether or not they see themselves as actually implicated in the latter’s historic mission and the people’s war which now seeks to fulfil it.
Faisal Al-Asaad
Source: Ebb Magazine